In today's interconnected world, privacy is paramount. Every website visit, every online interaction, begins with a fundamental process: Domain Name System (DNS) resolution. Traditionally, this process has been conducted over plain, unencrypted connections, leaving your browsing activity vulnerable to eavesdropping. Enter DNS over HTTPS (DoH), a technology designed to enhance your online privacy.
Understanding the DNS Landscape
Before diving into DoH, let's recap the basics of DNS. When you type a website address (e.g, example.com) into your browser, your computer needs to translate that human-readable name into an IP address (e.g, 93.184.216.34) that servers can understand. This translation is the job of DNS servers.
Traditionally, the communication between your device and the DNS server is unencrypted. This means anyone on the network, including your internet service provider (ISP), can see the websites you're visiting. This lack of privacy has significant implications for your online security and anonymity.
What is DNS over HTTPS (DoH)?
DoH addresses this vulnerability by encrypting DNS queries using the HTTPS protocol. Instead of sending DNS requests in plain text, DoH wraps them in an encrypted HTTPS connection. This prevents third parties from intercepting and viewing your DNS traffic.
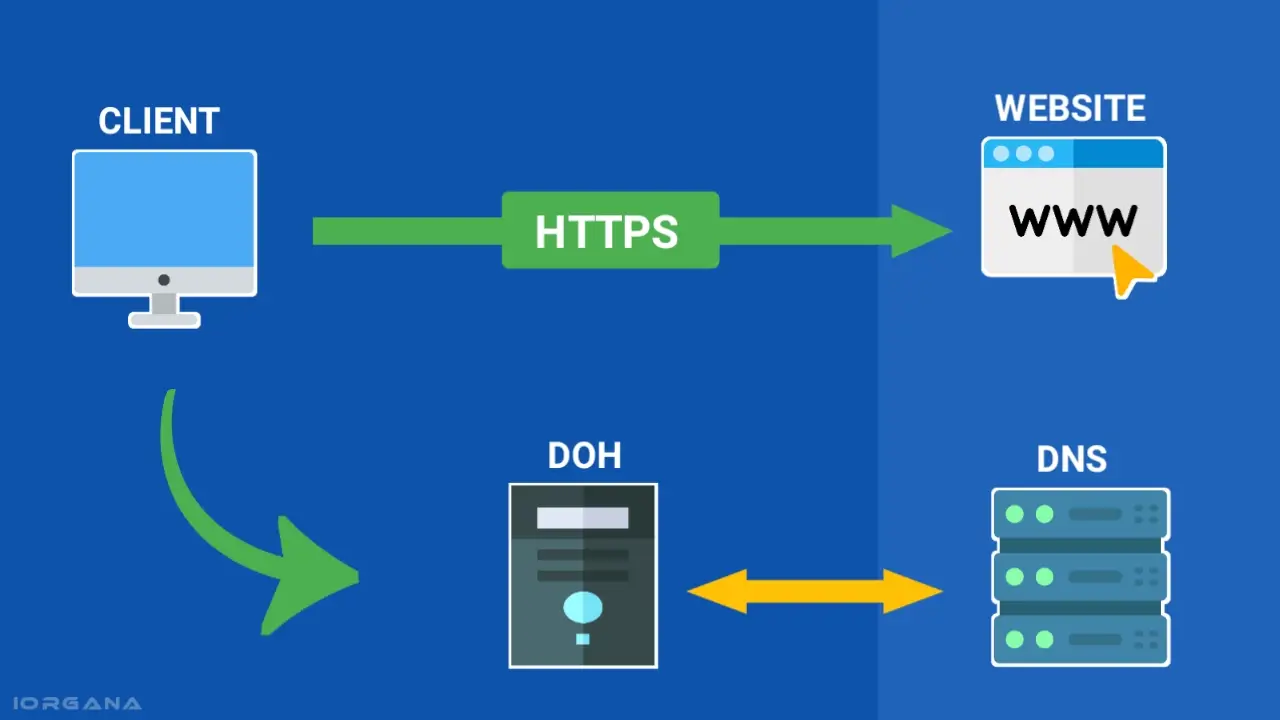
How DoH Works
Traditional DNS:
Your device sends a DNS query to your ISP's DNS server over UDP or TCP port 53 (unencrypted).
The ISP's server resolves the domain name to an IP address and sends the response back to your device.
Anyone monitoring the network can see the DNS queries and responses.
DNS over HTTPS (DoH):
Your device sends a DNS query to a DoH-enabled server over HTTPS port 443 (encrypted).
The DoH server resolves the domain name and sends the encrypted response back to your device.
Third parties cannot read the content of the DNS query or response.
Benefits of DoH
- Enhanced Privacy: DoH significantly improves your online privacy by preventing ISPs and other network observers from seeing your DNS queries.
- Protection Against Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Encrypting DNS traffic makes it harder for attackers to intercept and manipulate DNS responses.
- Circumventing Censorship: In some regions, ISPs may block access to certain websites by manipulating DNS records. DoH can help circumvent these restrictions.
- Increased Security: By encrypting DNS traffic, DoH reduces the risk of DNS spoofing and other attacks that rely on unencrypted DNS queries.
Considerations and Potential Concerns
- Centralization Concerns: Some critics argue that DoH could lead to the centralization of DNS resolution in the hands of a few large companies, potentially giving them excessive control over online traffic.
- ISP Visibility: While DoH protects your DNS traffic from your ISP, it shifts visibility to the chosen DoH provider. Choosing a reputable and privacy-focused DoH provider is crucial.
- Network Management Challenges: DoH can make it more difficult for network administrators to monitor and manage network traffic, which can be a concern in enterprise environments.
Implementing DoH
Most modern web browsers and operating systems support DoH. You can enable it in your browser's settings or configure it at the operating system level. Popular DoH providers include Cloudflare (1.1.1.1), Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8), and NextDNS.
Conclusion
DNS over HTTPS (DoH) represents a significant step forward in enhancing online privacy and security. By encrypting DNS traffic, DoH helps protect your browsing activity from prying eyes. While there are some considerations to keep in mind, the benefits of DoH make it a valuable tool for anyone concerned about their online privacy.
Try our related context products: DNS Changer and DNS Changer Plus.